
A Brief Introduction to Criminal Law (2nd Edition) Edit editionThis problem has been solved:Solutions for Chapter 3
Looking for the textbook?- CH1
- CH2
- CH3
- CH4
- CH5
- CH6
- CH7
- CH8
- CH9
- CH10
- CH11
- CH12
- 1PT
- 2PT
- 3PT
- 4PT
- 5PT
- 6PT
- 7PT
- 8PT
- 9PT
- 10PT
- 11PT
- 12PT
- 13PT
- 14PT
- 15PT
- 16PT
- 17PT
- 18PT
- 19PT
- 20PT
Theft: When the property is taken away through force (threatened or actual) or with the intention of stealing it (sneaking away without prior permission) is termed as theft. In other words, the physical removal of the property or any other object without the consent of the owner with the intention of depriving the owner of it permanently is termed as theft.
The trespassory taking away of personal goods from the possession of the owner with the intention of stealing is termed as Larceny.
Ownership: When the person has the title to the property is termed as ownership. Therefore, option b is incorrect.
Constructive asportation is the situation in which accused or forced an innocent party to move any property or money for him. Therefore, option c is incorrect.
Continuing trespass: When the person continues, the use of another property without proper authorization is termed as continuing trespassing. Therefore, option d is incorrect.
Possession: When the person has the broad and detailed discretion about the use of the property but does not hold the title or ownership of the property is termed as a possession. Therefore, option e is incorrect.
Custody: When the person does not possess the ownership or title of the property but does have the right to use the property, however, has no or little discretion about how and where to use the property is termed as custody. Therefore, option a is correct.
Therefore, the correct option is 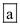 .
.
Corresponding textbook




