
2014 FASB Update Intermediate Accounting (15th Edition) Edit editionThis problem has been solved:Solutions for Chapter 5
Looking for the textbook?- CH1
- CH2
- CH3
- CH4
- CH5
- CH6
- CH7
- CH8
- CH9
- CH10
- CH11
- CH12
- CH13
- CH14
- CH15
- CH16
- CH17
- CH18
- CH19
- CH20
- CH21
- CH22
- CH23
- CH24
- 1AAP
- 1BE
- 1C
- 1CA
- 1CAC
- 1E
- 1EB
- 1FRP
- 1ICA
- 1ITQ
- 1P
- 1PB
- 1PR
- 1Q
- 2BE
- 2C
- 2CA
- 2E
- 2EB
- 2ICA
- 2ITQ
- 2P
- 2PB
- 2Q
- 3BE
- 3C
- 3CA
- 3E
- 3EB
- 3ICA
- 3ITQ
- 3P
- 3PB
- 3Q
- 4BE
- 4C
- 4CA
- 4E
- 4EB
- 4ICA
- 4ITQ
- 4P
- 4PB
- 4Q
- 5BE
- 5CA
- 5E
- 5EB
- 5ICA
- 5ITQ
- 5P
- 5PB
- 5Q
- 6BE
- 6E
- 6EB
- 6ICA
- 6P
- 6PB
- 6Q
- 7BE
- 7E
- 7EB
- 7ICA
- 7P
- 7PB
- 7Q
- 8BE
- 8E
- 8EB
- 8Q
- 9BE
- 9E
- 9EB
- 9Q
- 10BE
- 10E
- 10EB
- 10Q
- 11BE
- 11E
- 11EB
- 11Q
- 12BE
- 12E
- 12EB
- 12Q
- 13BE
- 13E
- 13EB
- 13Q
- 14BE
- 14E
- 14EB
- 14Q
- 15BE
- 15E
- 15EB
- 15Q
- 16BE
- 16E
- 16EB
- 16Q
- 17E
- 17EB
- 17Q
- 18E
- 18EB
- 18Q
- 19Q
- 20Q
- 21Q
- 22Q
- 23Q
- 24Q
- 25Q
- 26Q
- 27Q
- 28Q
- 29Q
- 30Q
- 31Q
- 32Q
A)
Balance sheet:
Balance sheet is a statement of financial position. It is one of the main reports in financial statements. It shows the financial position of a company. Balance sheet is prepared for a specific period. It summarizes the company’s assets, liabilities and shareholders’ equity. It is prepared by using accounting equation given below:
Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders’ Equity
P repare corrected balance sheet:
| H Co Corrected Balance Sheet As of 2014 | ||
| ASSETS | AMOUNT $ | AMOUNT $ |
| Current Assets | ||
| Cash | 59,500 | |
| Petty cash | 500 | |
| Inventory | 65,300 | |
| Account Receivables 38,500 | ||
| Less: bad debts 9,000 | 29,500 | |
| Long Term Investments | ||
| Bond sinking fund | 15,000 | |
| Property, plant and Equipment | ||
| Equipment 112,000 | ||
| Less: accumulated depreciation 28,000 | 84,000 | |
| Intangible Assets | ||
| Patent | 15,000 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | 291,300 $ | |
| LIABILITY | AMOUNT $ | AMOUNT $ |
| Current Liabilities | ||
| Accounts and notes payable | 52,000 | |
| Long term liabilities | ||
| Notes payable | 75,000 | |
| Stockholders’ Equity | ||
| Common stock | 100,000 | |
| Allowance for doubtful accounts | 13,500 | |
| Retained earnings | 50,800 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | 291,300 |
Steps to compute the balance sheet:
• Total assets are derived from current assets, long term investments, property, plant, and equipment, and intangible assets.
• The total liability is derived from current liability, long term debt, contributed capital, and retained earnings.
• The total assets and total liabilities should be equal in the balance sheet.
Working Note:
1.
Due to Bankruptcy Bad debts = $ 9,000
2.
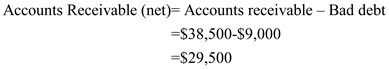
3.
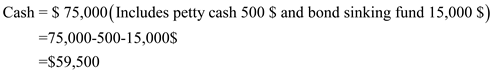
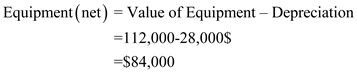
B)
ANALYSIS:
The information in the balance sheet provides useful information to the bank about the company’s ability to repay its loan. It is seen in the balance sheet that the company has sufficient amount of assets to pay its liabilities, and sufficient long term assets to meet its long term liability. Thus, Hopkins’s bank can grant a loan of amount $45,000.
C)
PRINCIPLES:
1. Monetary Unit Assumption
2. Time Period Assumption
3. Economic entity assumption
4. Cost principle
5. Full disclosure principle
6. Going concern principle
7. Matching principle
8. Revenue recognition principle
9. Materiality
10. Conservatism
The bank is likely to raise these objectives and principles regarding the usefulness for loan renewal.
Corresponding textbook




