
2014 FASB Update Intermediate Accounting (15th Edition) Edit editionThis problem has been solved:Solutions for Chapter 16
Looking for the textbook?- CH1
- CH2
- CH3
- CH4
- CH5
- CH6
- CH7
- CH8
- CH9
- CH10
- CH11
- CH12
- CH13
- CH14
- CH15
- CH16
- CH17
- CH18
- CH19
- CH20
- CH21
- CH22
- CH23
- CH24
- 1AAP
- 1BE
- 1CA
- 1CAC
- 1E
- 1EB
- 1FRP
- 1FSA
- 1ICA
- 1ITQ
- 1P
- 1PB
- 1PR
- 1Q
- 2BE
- 2CA
- 2E
- 2EB
- 2ICA
- 2ITQ
- 2P
- 2PB
- 2Q
- 3BE
- 3CA
- 3E
- 3EB
- 3ICA
- 3ITQ
- 3P
- 3PB
- 3Q
- 4BE
- 4CA
- 4E
- 4EB
- 4ICA
- 4ITQ
- 4P
- 4PB
- 4Q
- 5BE
- 5CA
- 5E
- 5EB
- 5ICA
- 5ITQ
- 5P
- 5PB
- 5Q
- 6BE
- 6CA
- 6E
- 6EB
- 6ICA
- 6P
- 6PB
- 6Q
- 7BE
- 7E
- 7EB
- 7ICA
- 7P
- 7PB
- 7Q
- 8BE
- 8E
- 8EB
- 8ICA
- 8P
- 8PB
- 8Q
- 9BE
- 9E
- 9EB
- 9ICA
- 9P
- 9PB
- 9Q
- 10BE
- 10E
- 10EB
- 10ICA
- 10Q
- 11BE
- 11E
- 11EB
- 11ICA
- 11Q
- 12BE
- 12E
- 12EB
- 12ICA
- 12Q
- 13BE
- 13E
- 13EB
- 13ICA
- 13Q
- 14BE
- 14E
- 14EB
- 14ICA
- 14Q
- 15BE
- 15E
- 15EB
- 15ICA
- 15Q
- 16BE
- 16E
- 16EB
- 16Q
- 17E
- 17EB
- 17Q
- 18E
- 18EB
- 18Q
- 19E
- 19EB
- 19Q
- 20E
- 20EB
- 20Q
- 21E
- 21EB
- 21Q
- 22E
- 22EB
- 22Q
- 23E
- 23EB
- 23Q
- 24E
- 24EB
- 24Q
- 25E
- 25EB
- 25Q
- 26E
- 26EB
- 26Q
- 27E
- 27EB
- 28E
- 28EB
- 29E
- 29EB
- 30E
- 30EB
a)
Prepare journal entry in the books of G to record the issuance of the bonds:
| Date | Particular | Debit | Credit |
| January 1, 2013 | Cash Bonds Payable (To Record issuance of 6% bonds at par) | $200,000 - | - $200,000 |
Note:
G issued 10-year, $200,000 face value, 6% bonds at par.
b)
Prepare statement showing computation of Basic Earnings per share (EPS) and diluted earnings per share:
| Basic EPS | 2014 | 2013 |
| Net Income(a) | $30,000 | $27,000 |
| Outstanding shares(b) | 10,000 | 10,000 |
| Basic EPS( a / b) | $3.00 | $2.70 |
Diluted Earnings per share (EPS) for G 2014 and 2013:
| Diluted EPS | 2014 | 2013 |
| Net Income | $30,000 | $27,000 |
| Add: Interest savings ($200,000 | 12,000 | 12,000 |
| Adjusted net income (a) | $42,000 | $39,000 |
| Outstanding shares | 10,000 | 10,000 |
| Shares upon conversion (200 | 6,000 | 6,000 |
| Total shares for Diluted EPS (b) | 16,000 | 16,000 |
| Diluted EPS ( a / b ) | $2.63 | $2.44 |
NOTE:
So, for 2014, Basic EPS is $3.00 compared to $2.70 in 2013 and
For Diluted EPS is $2.63 in 2014 and $2.44 in 2013
c)
Prepare journal entry in the books of G to record the conversion of the bonds with assumption that 75% of holders of G’s convertible bonds on June 30, 2015:
| Date | Particulars | Debit | Credit |
| June 30, 2015 | Bond conversion Expense Bonds Payable Common stock Paid-in-capital in Excess of par – Common stock Cash (To Record conversion of 75% bonds ) | $300 $150,000 - - - | - - $9,000 $141,000 $300 |
Note:
• Bonds converted are $150,000 ($200,000 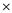 75%)
75%)
• Total number of bonds are 150 bonds ($150,000 / $1,000)
• New share issued are 4,500 (150 bonds 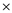 30 shares per bonds)
30 shares per bonds)
• Increase in common stock account is $9,000 (4,500 shares 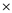 $2 par value)
$2 par value)
• Increase in paid-in-capital account is $141,000 ($150,000 - $9,000)
• Bond conversion expense is $300 ($150 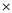 $2 per bond)
$2 per bond)
ANALYSIS:
Compare Net Income and Earnings per Share for 2014 and 2013 Relate to Basic and Diluted EPS:
| Items | 2014 | 2013 |
| Net Income | $30,000 | $27,000 |
| Basic Earnings Per Share | $3.00 | $2.70 |
| Diluted Earnings Per Share | $2.63 | $2.44 |
Importance of GAAP for EPS:
• GAAP follow the same model for recognizing stock-based compensation.
• The fair value of shares and options awarded to employees is recognized over the period to which the employees’ services relate to the matter.
• Calculation of basic and dilutive earnings per share is almost same between the IFRS and GAAP which help in comparison.
• Boards are working to solve the few difference which is minor in the calculation of earnings per share (EPS)
• One of the proposals is given in the FASB projects concerns contracts that can be settled in either cash or shares.
• Whereas under the GAAP companies provides chance of choice.
As per the analysis basic earnings per share in 2014 is $3 compared to $2.70 in 2013 which is superior, and benefit to the organization.
• Convertible bonds can be changed into other corporate securities during the some specified period of time after issuance. A convertible bond combines the benefit of a bond with the privilege of exchanging it for stock at the holder’s option.
• If the value of the stock appreciates significantly than the investor purchase, the security of a bond holding must guaranteed interest and principal plus the added option of the conversion.
• Corporation’s issued the convertible for the two main reason:
• In order to raise equity capital without giving up more ownership control to the group of investors or the investor.
• The important reason to raise the convertible is to obtain debt financing at the cheaper rates.
• Many companies could issue debt only at high interest rates unless they attach a convertible covenant.
• The FASB and IASB have analysis the accounting for financial instruments with features of both the debt and the equity.
• In the past, the boards proposed an explanation of equity which is far more restrictive than the current practice.
• But under the proposed “basic ownership approach”, only the common stock is classified as an equity.
• All the other instruments like preferred stock, options, and convertible debt are classified as liabilities.
• If the instruments is classified as liabilities are measured as fair value, and if any changes are reported as income.
• If the narrow analysis, it provides fewer opportunities to structure instruments and arrangements to achieve a desired accounting treatment.
• At last boards have agreed on some provisions to improve and simplify the financial reporting requirements for financial instruments with features of debt and equity.
• There are three accounting for convertible debt involves reporting issues at the time of
(1) Issuance
(2) Conversion
(3) Retirements
• Boards further detailed investigation for more improvement in these matters.
Prepare Journal entry in the books of Garner to record the issuance of the bonds:
| Date | Particulars | Debit | Credit |
| January 1, 2013 | Cash Bonds Payable (To Record issuance of 6% bonds at par) | $200,000 - | - $200,000 |
Note:
G issued 10-year, $200,000 face value, 6% bonds at par.
• As per the analysis, the bonds payable is credited and the cash is debited at 6% bonds at par.
• Convertible bonds can be changed into other corporate securities during specified period of time after issuance.
Corresponding textbook

 6% )
6% ) 30)
30)


